1. Enable Network Connectivity to the SAMBA ServerUsing the Fedora Network Configuration tool you will need to ensure that the ethernet card is enabled and properly functioning. Get quick access to the tool through this command: system-config-network
Once in the Network Configuration tool, you should ensure that your ethernet device is enabled. If it is not, select the eth device and then click on the Edit button. This will allow you to input the vital network adapter settings including: statically set IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. You should also select the top checkbox labeled Activate device when computer starts.
Close and save any changes you've made. The main goal is to ensure you have an ACTIVE and functioning network card on the SAMBA server.
Restart the network services or simply reboot your SAMBA server. Now try a ping to the server from another PC on the same subnet. At a command prompt, for example, type: ping 192.168.1.1
The ping should come back good validating your network connection.
 2.Update Firewall Settings
2.Update Firewall SettingsIn most cases the default Firewall setting on the SAMBA server locks out any inbound network requests. I've had a great many people come running to me about this issue. If you're setting up a basic SAMBA server within your business intranet, allow your ethernet connection to be a trusted device so others can get to your SAMBA server and not be bounced by the server's Firewall.
If you plan to use the SAMBA server outside of your business firewall/intranet you should NOT follow the next step. Instead you allow your local server to receive packets by making changes to your IPTABLES, such as:
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0 -j ACCEPT
The following step is for those using an intranet business server configuration.
Okay, now to allow your intranet based SAMBA server to properly accept incoming requests, from your Main menu choose System Settings, then Security Level. You can access this also by typing the command:
system-config-securitylevel
Please select the box next to the ethernet card you are using for intranet connectivity so that it becomes a TRUSTED DEVICE. Otherwise you have a super secure server that bounces inbound requests. Notice, this selection effects all the items in the Services listing above it, so please be careful in what context you allow a trusted device!
Press OK when finished.
 3.Enable SMB Services
3.Enable SMB Services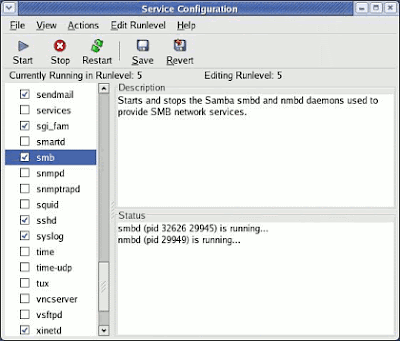
Ironically, the SMB daemon and other core services are usually NOT started by default. You will need to change this so that your SMB daemon is now started.
Using the GUI from the main menu, go to System Settings, then Server Settings, then choose Services. You can also get to this using the command: system-config-services
While you're looking over this long list of services, please DISABLE things you know for sure you do not need to run on this SAMBA server. For instance apmd, isdn, etc. But also ensure that key services such as SMB are selected and RUNNING. Select SMB and press the Start button. If it is supposedly already running you can press the Restart button to be sure it is indeed running correctly now.
Now press the Save button to make sure the configuration changes have been saved for future restarts.
Sometimes using the GUI just does not properly restart the SMB daemon. In such odd cases, I want to suggest you force a manual restart from the command line with this command: /etc/rc.d/init.d/smb restart
If you keep having startup failures, where for every reboot you need to perform Step 3, you may need to manually configure your start up processes so that SMB will always be in the init.d bootup..
 4.Create Server Users & Directories
4.Create Server Users & DirectoriesYou will need to ensure that people also have a login to the SAMBA server to do their work. Logins should be provided on an as needed basis. Obviously, in most cases the users accessing the SAMBA server will be a subset of the total users on the Windows business network.
Create user logins with the Gnome User Manager tool in Fedora. You can find this from the main menu by choosing System Settings, then Users & Groups. The command for this is: system-config-users
Notice this is the first step in creating SAMBA users, which comes later.
Add as many users as you need and then move on to the next part, which is creating directories (aka. folders) for use.
This is such an obvious step most people usually forget to think about it before hand. However, it is very helpful to think ahead what directories you will allow access to on the SAMBA Server for business use. In my case the people needing SAMBA server access will be updating webpages. Therefore, I do not need to add any other folders for file sharing or group interaction. Be sure you add any folders in a reasonable and ordered fashion.
A big TIP for those who are not aware, the permissions settings for your folders are very important
 5.Configure the SAMBA Server
5.Configure the SAMBA ServerIt's time to configure your SAMBA server to allow others on the intranet to login and use the server from Windows or Linux PCs.
From the main Fedora menu, choose System Settings, then Server Settings, then Samba. You can also get to this tool by typing the command: system-config-samba
You are about to make changes to the SAMBA Configuration file called smb.conf. This file is found under /etc/samba. I also want you to be aware that you can edit configuration files with the web interface tool called Samba Web Administration Tool(SWAT) and several others. Now lets move ahead using the Configuration tool using the preloaded Fedora tools. NOTICE that many people begin by tinkering with their .conf file... this is NOT a good idea. First ensure that the basic samba connectivity works and THEN you can tinker with the smb.conf (see troubleshooting below)
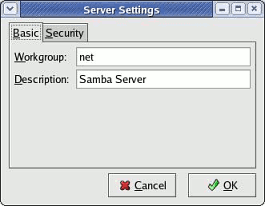
A. Begin by Making Changes to the Server Settings
Under the Preference menu item choose Server Settings...
Be sure to include the Windows workgroup name. In the example above the workgroup has been changed to net. Your situation may be different. In many cases naming the workgroup simply workgroup is fine, so long as your Windows PCs connect to this same name.
Under this same window, click on the Security tab. It comes by default with the appropriate settings for a basic SAMBA Server. The Authentication mode should be User. You would need to change this only if you plan to allow logins based on the Microsoft ADS.
Press OK to finish making basic changes to the server.
B. Select SAMBA Users
Under the Preference menu item choose Samba Users
In this window you must Add at least one user who will have access to the SAMBA Server. Notice that only user accounts you created in step 4 should be added to this listing.
Press the Add User button, then from the pull down select a user. Fill out the additional information needed for this SAMBA user. Press OK when finished.
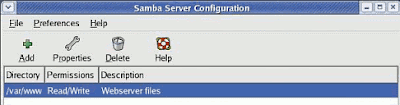
C. Adding A Shared Folder
Under the SAMBA Server Configuration window, you must create at least one SAMBA share directory.
Press the Add button and then the Browse button. Now choose a folder you wish to make available to SAMBA users. Be careful, some folders have permissions settings that do not allow sharing. Now be sure to select the Read/Write option to allow people full access. Don't press OK yet!
You should see your shared folder appear under the listing as shown in the example above.
D. Adding Users
In the same window, select the second tab labeled Access. From here choose the first option labeled Only allow access to specific users and select the users you wish to give access to this specific SAMBA shared folder. Press OK when finished.
You can repeat steps C and D for each new shared folder.
Once completed, please choose File from the menu then choose Quit.
Hopefully this saved all of your settings properly. If you encounter issues with the graphic SAMBA configuration tool, such as it failing to accept your changes, then please read the Troubleshooting Tip 4 located below.
 6.Restart the SAMBA Services
6.Restart the SAMBA ServicesNow you need to restart all SAMBA services. You can use the process found in Step 3, except press the Restart button or use the word restart instead of the word start.
I mentioned earlier that sometimes your changes do not get properly picked up. I've installed so many different Fedora SAMBA configurations that I can't recall every reason. This may be a very good time to simply reboot the LINUX/SAMBA Server. Rebooting will ensure everything gets properly started up and all of the configuration changes are included. More importantly, this is likely the last time you will ever restart your SAMBA server again. Some of my FEDORA servers haven't been restarted in years.
 7.Access the SAMBA Server from Windows
7.Access the SAMBA Server from WindowsYou're now ready to fully utilize your new intranet SAMBA Server for work. On any Windows PC you can access the server by simply going to the main Start menu, choosing Run and typing in the hostname of your SAMBA server. For example: \\linuxserver
Please notice that in the Windows environment you use different slashes and you need to ensure this syntax.
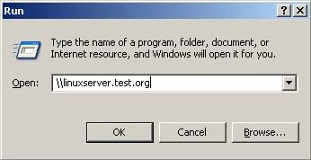
If this does not work, perhaps if the server is not yet included in your DNS, try accessing the SAMBA Server through its IP address: \\192.168.1.2
Obviously you need to use an actual hostname or IP address and not my example.
If all works well you should instantly see a SERVER LOGIN window. Now login using a SAMBA created username.
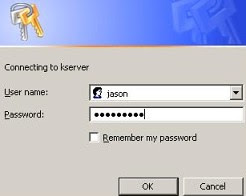
You should then instantly see the shared folder as well as the individual user's personal folder that exist on the SAMBA Server.
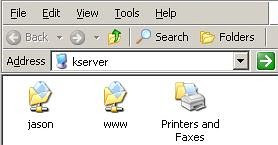
The samba file server in the windows ‘My Network Places

’
8.EDITING THE SMB.CONF FILEIf you must edit the smb.conf file here are a few pointers:
1. Find your smb.conf file
The smb.conf file contains the key elements for configuring your SAMBA server. It is almost always located in the directory /etc/samba and so you get to it with the command: cd /etc/samba
2. Edit the smb.conf file
First use this command to make a backup of your file: cp smb.conf smb.conf.backup
3. Now edit the smb.conf file using your favorite text editor.
One of the most important lines is this:
# workgroup = NT-Domain-Name or Workgroup-Name
workgroup = workgroup
Be sure that the workgroup matches the Windows workgroup you want this server in. In the example it is set to “workgroup”.
If you're editing this file to allow for WindowsNT or ADS usernames, be sure next to wins server you specify the correct LINUX server IP address:
wins server = 192.168.1.2
The Share Definitions section is MOST VITAL. Under this section you must at least ensure that the username file is mapped correctly. In the basic example I am writing about you will map to the standard SAMBA username file.
username map = /etc/samba/smbusers
Notice that I've removed the ; so this parameter is actually used.
Now test that every change you've made at least passes the parameter test. At the command prompt type:
testparm
You should see zero errors.
4. Don't forget once you edit the smb.conf file you either need to run the command:
/etc/rc.d/init.d/smb restart
or you can simply reboot the server. But please do one of these or your changes will not get picked up!
 9.TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
9.TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS1. SAMBA Server is not accessible
First and foremost try a reboot to the server itself! It is vital you do this before someone talks you into changing configs, playing with your network card settings etc. Just reboot and try again to see if it clears up the issue.
2. Network Unreachable or Host Unreachable From Linux PCs
Trying to connect from another Linux PC and nothing happens or "network unreachable" may be as ridiculous as an incorrect SAMBA connection. Make absolutely certain that the connection is typed in exactly as follows (obviously changing the workgroup name to your windows workgroup): smb://WORKGROUP
On some KDE desktops, attempts failed because the syntax incorrectly tries: smb:/workgroup Those // are quite important!
3. Failure to Connect from Windows PCs
Not connecting to the server from Windows PCs may be a result of bad network configuration. Are you absolutely certain you entered the correct network details? Please double check to make sure that you have a proper hostname for the Samba server, that you have a working IP address, and the correct Subnet and Gateway included. In most cases these last two should simply match what your windows PCs have designated.
4. Changes to the configuration are not being picked up
The Gnome SAMBA Configuration GUI often encounters errors when trying to update new SAMBA settings. I've seen the GUI tool write a whole lot of garbage into the SAMBA configuration file (smb.conf). For this reason, as I mentioned earlier, you may need to start with a fresh clean smb.conf file and try again, or you may need to manually adjust settings without the GUI.
5. Can't Share Folder in Home Directory
First, it's always a good idea NOT to make a Samba share out of directories inside your Home folder for security reasons. Making unique share folders is often the best bet. However, there are times when you need to share a folder and the way to do so is to update your Samba Share's security settings. Under the Samba Configuration, highlight your shared directory and press Properties. Here you can see the "Basic Permissions" list and usually the default is "Read Only." Select the "Read/Write" option and be sure to save your changes by quitting and then restarting the smb daemon. If this doesn't resolve the issue of directory shares, you may have a more fundamental security issue. You need to ensure that the over all Samba security settings under "Preferences", then "System Settings" and then the Security tab are correct.
10.INTEGRATING WITH MICROSOFT ADS OR NT LOGINS
Maybe at this point you're in dire need to figure out how to use the SAME exact logins/password for users on the LINUX/SAMBA server as in the rest of your ADS environment. I promised I would avoid the details of this but here are some helpful tips. In the smb.conf file you will need to add the obvious configuration lines for ADS, but also be sure to change this line:
unix password sync = yes